The check engine light is perhaps one of the most dreaded warning symbols that can illuminate on the dashboard of Toyota Tacoma. In this article, we will delve into the most common causes behind the check engine light.

The check engine light illuminates in Toyota Tacoma when the on-board diagnostic system detects a problem with the engine or emissions system. If left unchecked, the issue could cause more serious problems and result in costly repairs.
Static CEL: A static check engine light  in Tacoma means that there is a problem with the engine or emissions system, but it is not an urgent issue. The vehicle can typically be driven safely for a short period of time, but it should be taken to a mechanic soon to avoid further damage or increased emissions.
in Tacoma means that there is a problem with the engine or emissions system, but it is not an urgent issue. The vehicle can typically be driven safely for a short period of time, but it should be taken to a mechanic soon to avoid further damage or increased emissions.
Flashing CEL: When the check engine light  is flashing in Tacoma, it indicates that there is a significant problem with the engine that requires immediate attention. The flashing light often indicates a misfire, which can cause damage to the catalytic converter. When this happens, the engine should be turned off immediately to prevent further damage.
is flashing in Tacoma, it indicates that there is a significant problem with the engine that requires immediate attention. The flashing light often indicates a misfire, which can cause damage to the catalytic converter. When this happens, the engine should be turned off immediately to prevent further damage.
1. Loose or bad gas cap
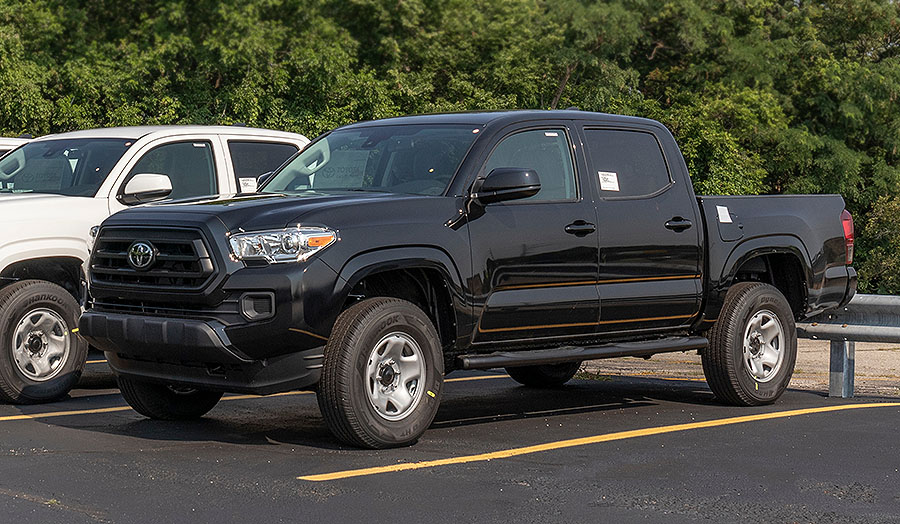
It is possible for the check engine light to come on in Tacoma due to a loose or bad gas cap. The fuel system in modern vehicles is designed to maintain a certain level of pressure, and if the gas cap is not sealing properly, it can cause a leak and disrupt the pressure balance in the system. This can trigger the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system, which may illuminate the check engine light.

Tighten the gas cap
If you suspect that your gas cap may be the cause of the problem, you can try tightening it to see if the light goes off. If the cap is damaged or worn out, it may need to be replaced. In either case, once the issue has been resolved, you may need to drive your Tacoma for a few miles to allow the onboard computer to reset itself and turn off the check engine light.
No gas cap?
In vehicles with capless gas tanks, a check engine light related to the fuel system can still occur, even though there is no traditional gas cap. The light is usually triggered by issues with the fuel filler neck that connects the fuel tank to the fuel inlet. If there are obstructions, damage, or leaks in the filler neck, it can trigger a check engine light.
If the light remains on in your Tacoma even after addressing the gas cap issue, it is possible that there is another underlying problem that needs to be diagnosed.
2. Faulty O2 sensor
A faulty upstream oxygen (O2) sensor can cause the check engine light to come on in Toyota Tacoma. The oxygen sensor is an important component of the vehicle’s emissions control system, and it monitors the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. The engine control module (ECM) uses this information to adjust the air/fuel ratio, ensuring that the engine is running efficiently and within emissions limits.

Symptoms of bad O2 sensor
If the oxygen sensor is faulty or has failed in Tacoma, it can cause the ECM to receive inaccurate readings, which can result in the check engine light being triggered. Common symptoms of a faulty O2 sensor include poor fuel economy, rough idling, and a decrease in engine performance.
If you suspect that your O2 sensor may be the cause of the problem, it is best to have it diagnosed and replaced as soon as possible. A faulty O2 sensor can cause the engine to run inefficiently, which can lead to increased emissions, decreased fuel economy, and potentially more serious engine problems if left untreated.
Bad O2 sensor can damage the catalytic converter
A bad O2 sensor can cause damage to the catalytic converter over time. The catalytic converter in Tacoma is designed to reduce harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful gases before they exit the exhaust system. However, if the engine is not running efficiently due to a bad O2 sensor, excess unburned fuel can enter the catalytic converter and cause it to overheat, melt, or clog.
Recommended video
3. Dirty or defective MAF sensor
A dirty or defective Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor can also cause the check engine light to come on in Toyota Tacoma. The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine and sends this information to the engine control module (ECM). The ECM then uses this information to adjust the fuel injection and ignition timing to optimize engine performance and reduce emissions.
Symptoms of bad MAF sensor
If the MAF sensor is dirty or defective, it can send inaccurate information to the ECM, which can result in poor engine performance, reduced fuel economy, and potentially damage the catalytic converter. Symptoms of a dirty or defective MAF sensor in Tacoma can include hesitation or stalling when accelerating, rough idling, and reduced engine power.
Clean or replace the MAF sensor
Cleaning the MAF sensor with a specialized cleaner can sometimes help restore proper function, but if the sensor is damaged or has failed, it will need to be replaced.
Recommended video
4. Bad spark plugs
Bad spark plugs can cause a number of engine performance issues and can also trigger the check engine light in Tacoma.
Spark plugs play a critical role in the ignition process by creating a spark that ignites the fuel/air mixture in the combustion chamber. Over time, spark plugs can become fouled or worn, which can lead to decreased engine performance, reduced fuel economy, and other problems.
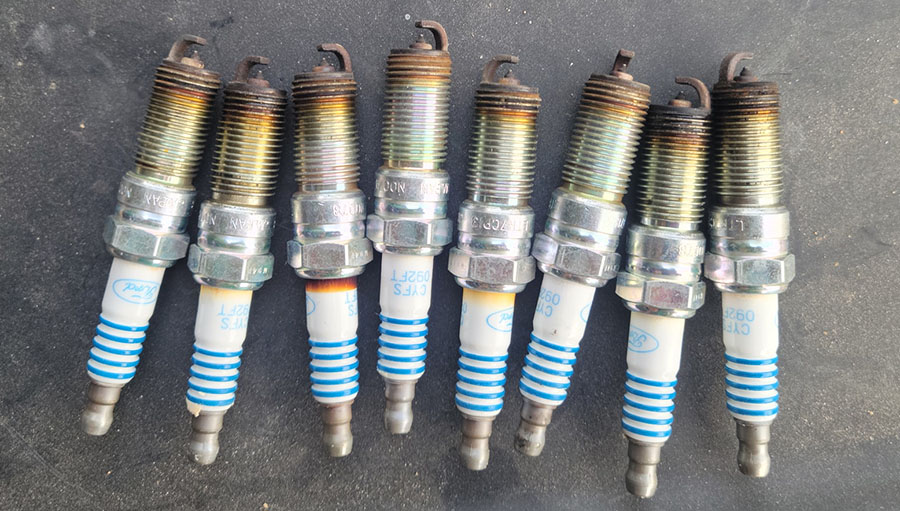

Symptoms of bad spark plugs
Symptoms of bad spark plugs in Tacoma can include rough idling, engine misfires, decreased acceleration, and poor fuel economy. In some cases, a bad spark plug can cause the check engine light to come on, indicating a problem with the engine’s emissions control system.
If you suspect that your Tacoma spark plugs may be the cause of the problem, it is best to have them inspected and replaced if necessary. Regular maintenance and inspection of the spark plugs can help to prevent engine performance issues and ensure that the engine is running efficiently.
Recommended video
5. Bad ignition coils
Bad ignition coils can also cause engine performance issues and can trigger the check engine light in Toyota Tacoma. The ignition coils are responsible for converting the low voltage from the battery into the high voltage needed to create a spark at the spark plugs. Over time, ignition coils can become worn or damaged, which can cause engine misfires, decreased acceleration, and poor fuel economy.
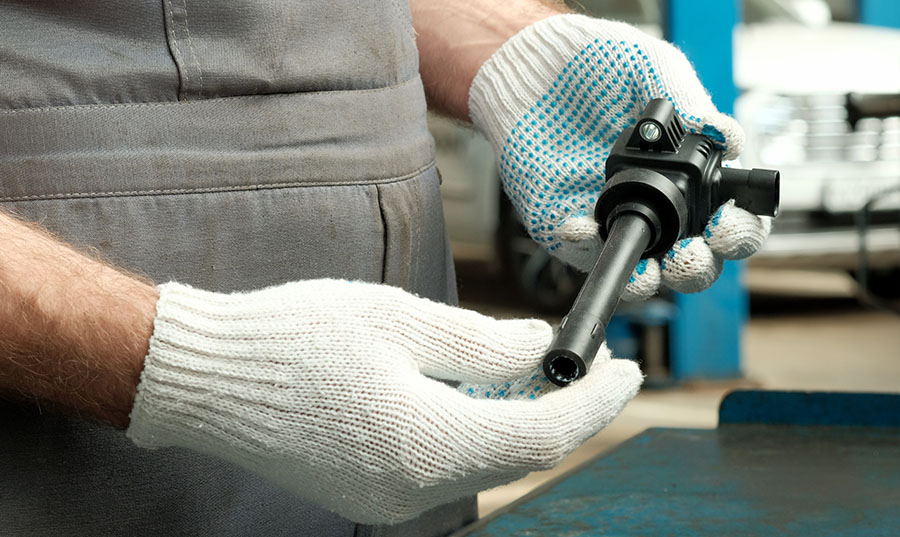

Symptoms of bad ignition coils
Symptoms of bad ignition coils in Tacoma can include rough idling, engine misfires, decreased acceleration, and poor fuel economy. Engine misfires can occur when the ignition coil fails to provide enough voltage to the spark plug, causing the engine to run rough or hesitate. You may feel a vibration or jerkiness in the vehicle as a result of these misfires.
Recommended video
6. Vacuum leak
A vacuum leak can affect engine performance and trigger the check engine light in Tacoma. The engine vacuum is an essential component of the vehicle’s emission control system, and a leak in the vacuum system can cause a range of issues.
Symptoms of a vacuum leak can include rough idling, engine misfires, decreased acceleration, and poor fuel economy.
Vacuum leak may be difficult to diagnose
Diagnosing a vacuum leak can be a challenging task in your Tacoma, as it may require specialized equipment and expertise. Mechanics may use smoke machines, vacuum gauges, or other diagnostic tools to pinpoint the location of the leak. Once the leak has been located, the damaged or worn component can be replaced, such as a vacuum hose, gasket, or intake manifold.
7. Bad compression
Bad compression is a serious engine problem that can cause a range of symptoms in Toyota Tacoma, including rough idling, engine misfires, decreased acceleration, poor fuel economy, and check engine light. Compression is the pressure that builds up inside the engine’s cylinders during the combustion process, and if this pressure is not sufficient, it can lead to a range of performance issues.
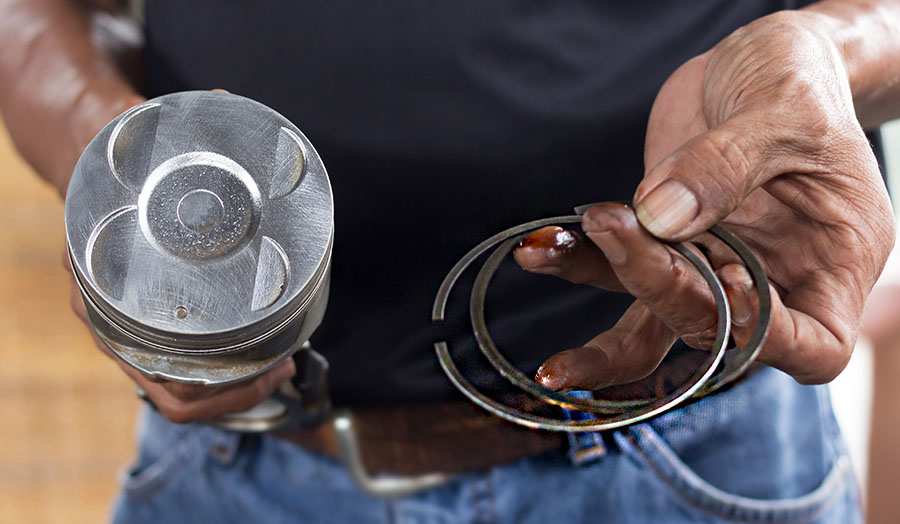

Causes of bad compression
Common causes of bad compression in Tacoma include worn piston rings, worn or damaged cylinder walls, a blown head gasket, or bent or warped valves. If the engine is not able to maintain proper compression levels, it may struggle to start, run rough, or fail to accelerate properly.
Diagnosing bad compression
To diagnose a compression problem in Tacoma, a mechanic will usually perform a compression test, which measures the amount of pressure inside each cylinder. If the pressure is not within the manufacturer’s recommended range, it may indicate a problem with the engine’s compression.
Repairing a compression problem in Tacoma can be a complex and expensive process, and it may involve rebuilding or replacing major engine components. In some cases, a compression problem may be a sign that the engine has reached the end of its useful life and needs to be replaced.
Perform regular maintenance
Regular maintenance of your Tacoma, including oil changes and tune-ups, can help to prevent compression problems and ensure that the engine is running efficiently. If you suspect that your vehicle has a compression problem, it is important to have it inspected and repaired as soon as possible to void further damage to the engine.
8. Carbon buildup
Carbon buildup is a common engine problem in high mileage vehicles that occurs when carbon deposits accumulate on the internal engine components, such as the intake valves, fuel injectors, and combustion chamber. This buildup can affect engine performance and fuel economy, and can also cause the check engine light to come on in Tacoma.
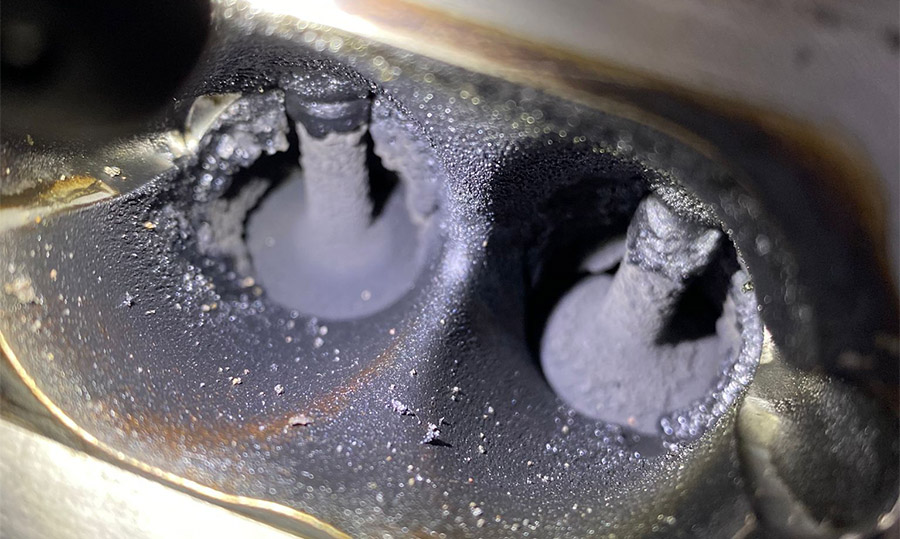

Symptoms of carbon buildup
Symptoms of carbon buildup in Tacoma can include rough idling, decreased acceleration, poor fuel economy, and increased emissions. Over time, carbon buildup can cause serious engine damage, such as engine knock or misfires.
Diagnosing carbon buildup
To diagnose carbon buildup in Tacoma, a mechanic may inspect the engine components and perform a fuel system cleaning or an engine decarbonization procedure. This may involve removing the intake manifold and manually cleaning the components or using a specialized cleaning agent to remove the carbon buildup.
How to prevent carbon buildup
Preventing carbon buildup is essential for maintaining engine performance and fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance of your Tacoma, such as changing the engine oil and air filter, can help prevent carbon buildup. Additionally, using high-quality fuel and avoiding short trips or idling can help prevent carbon buildup from occurring.
9. Bad fuel injectors
Fuel injectors are responsible for delivering fuel to the engine in a precise and controlled manner, and if they become clogged or dirty, they may not be able to deliver the proper amount of fuel to the engine. This can cause engine knock or misfires and can illuminate the check engine light in Tacoma.
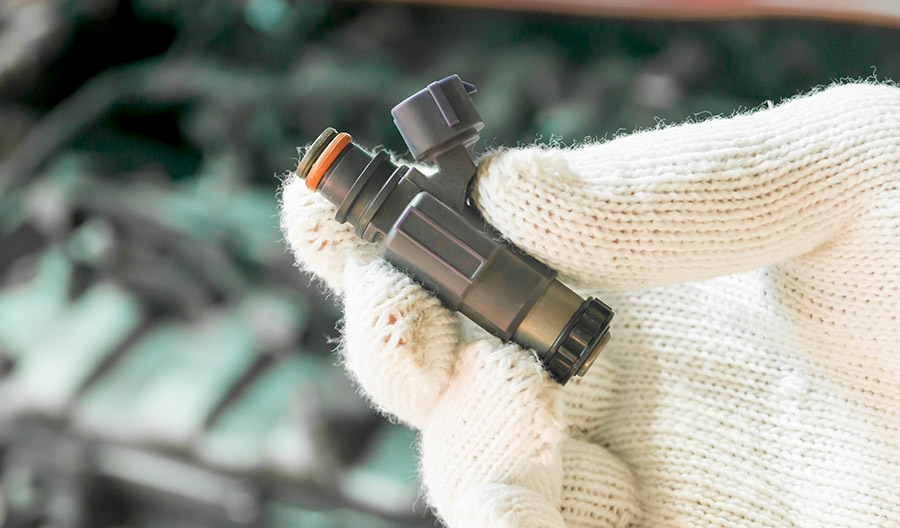

Causes of clogged fuel injectors
Clogged fuel injectors in Tacoma can be caused by a variety of factors, including the use of low-quality fuel, a dirty fuel filter, or the accumulation of dirt and debris inside the fuel system. Over time, clogged fuel injectors can cause serious engine damage.
Diagnosing clogged fuel injectors
To diagnose clogged fuel injectors in Tacoma, a mechanic may perform a fuel system cleaning or use specialized equipment to test the injectors’ flow rates and spray patterns. If the injectors are clogged or damaged, they may need to be removed and cleaned or replaced.
10. Poor quality gas
Using poor quality gas in your Tacoma can cause a range of engine problems and affect vehicle performance. When gasoline contains impurities, such as water or sediment, it can cause engine misfires, rough idling, decreased acceleration, and poor fuel economy. Additionally, poor quality gas can cause damage to engine components, such as the fuel injectors or fuel pump, which can lead to more serious engine problems over time.

It is important to purchase fuel from reputable gas stations and to use high-quality gas that meets the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Use an OBD scanner for diagnosis
Using an OBD scanner is an effective way to diagnose engine problems and determine the cause of the check engine light in Toyota Tacoma. OBD stands for “On-Board Diagnostics,” and an OBD scanner is a handheld device that can communicate with the vehicle’s onboard computer to read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
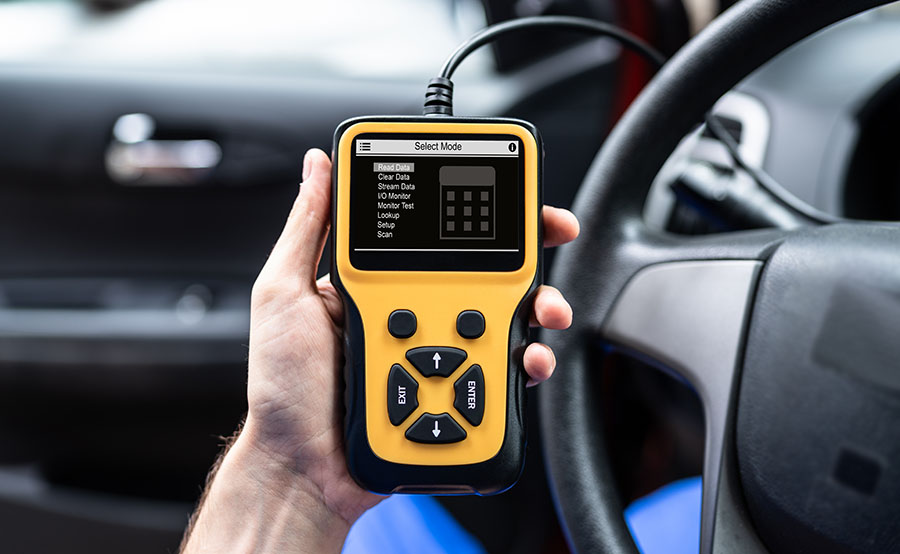

When the check engine light comes on, it typically indicates that a problem has been detected in one of the vehicle’s systems. The onboard computer stores a corresponding DTC, which can be read by an OBD scanner to determine the cause of the problem. Once the cause of the problem has been identified, the appropriate repairs can be made to fix the issue.
Using an OBD scanner is a straightforward process that can be done by most vehicle owners. First, locate the vehicle’s OBD-II port, which is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Plug the OBD scanner into the port and turn on the ignition (without starting the engine). The scanner should power on and prompt you to enter the vehicle information.
Once the vehicle information has been entered, the scanner will read and display any stored DTCs. The scanner may also display a description of the code and possible causes. This information can be used to diagnose the problem and determine the appropriate repairs.
It is important to note that while an OBD scanner can be a helpful tool in diagnosing engine problems, it may not always provide a definitive answer. In some cases, additional testing and inspection may be necessary to fully diagnose the problem. If you are unsure about using an OBD scanner or diagnosing engine problems yourself, it is recommended to seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic.
Resetting check engine light
An OBD scanner can be used to clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and reset the check engine light in Tacoma. However, it is important to note that simply clearing the codes and resetting the light does not fix the underlying problem that caused the codes to appear in the first place.
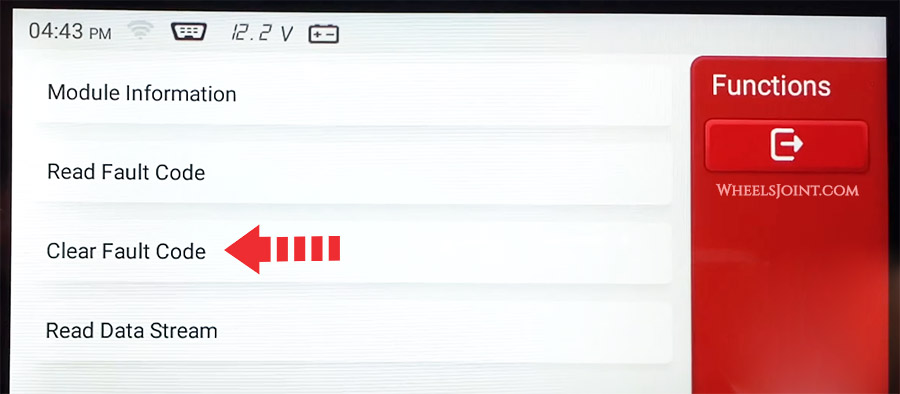
Check engine light will turn on again if the underlying issue is not fixed.
Clearing the codes and resetting the light can be helpful in some situations, such as if a temporary glitch in the system caused the codes to appear, but it is not a permanent solution. If the underlying problem is not fixed, the codes will likely reappear and the check engine light will come back on.
Additionally, some states and regions require that emissions-related codes be fixed before the vehicle can pass a smog check or emissions test. Simply clearing the codes and resetting the light without fixing the problem may cause the vehicle to fail the emissions test.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I drive my Tacoma with check engine light on?
Driving your Tacoma with the check engine light on is generally not recommended. The check engine light is an indicator that something is wrong with your vehicle’s engine or emission control system. While the issue may be minor in some cases, it could also indicate a more serious problem that requires immediate attention, especially if the check engine light is flashing.
Can a check engine light go off by itself?
Yes, in some cases, the check engine light may turn off on its own. The check engine light is designed to alert you when a fault is detected in your vehicle’s engine or emission control system. Once the issue is resolved or no longer detected during subsequent engine cycles, the light may automatically turn off.
How long will check engine light stay on after tightening gas cap?
After tightening the gas cap, it may take a certain amount of time and driving cycles for the check engine light to turn off. Typically, it takes a few minutes of driving for the light to go off if the gas cap was the issue causing the light to illuminate.
Can a dirty oil filter cause check engine light to come on?
A dirty or clogged oil filter is typically not a direct cause of the check engine light coming on in Tacoma. However, it can indirectly contribute to engine-related problems that might illuminate the light. For example, a clogged oil filter can restrict the flow of oil to the engine, resulting in decreased lubrication and potential damage to engine components.
What is the code for the gas cap check engine light?
The most common diagnostic trouble code (DTC) associated with a gas cap problem is P0442, which indicates a small leak in the evaporative emission control system.