The Audi e-tron (internal type designation GE ) is a battery-powered upper-class SUV from German automobile manufacturer Audi AG. The model was launched on September 17, 2018 in San Francisco. Deliveries started in March 2019; it was originally scheduled to start in late 2018.

History
The first concept vehicle, the Audi e-tron quattro concept, was presented at the IAA in autumn 2015.

Originally, the concept should have been made into production car at the Audi Summit on August 30, 2018 Brussels, but this was canceled.
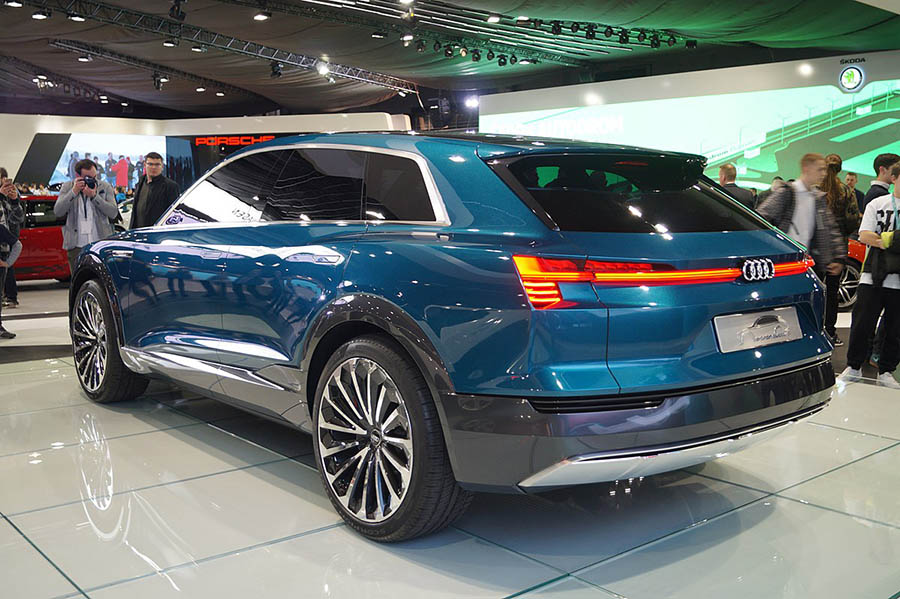

Production of the vehicle started on September 3, 2018 at CO2-neutral Audi Brussels plant. The premiere of the Audi e-tron was postponed and finally took place on September 17, 2018 in San Francisco. The formal trade fair premiere took place at the Paris Motor Show in October 2018. A short time later it became known that the Audi e-tron could not be delivered to the first customers as planned in 2018 because software problems delay delivery by at least four weeks. The first vehicles were delivered to customers from March 2019.
In June 2019, Audi launched a worldwide recall for the Audi e-tron. The reason: due to a faulty seal on the low-voltage cable, moisture can penetrate into the lithium-ion battery. This causes the orange battery warning light to come on; Fast charging is then no longer possible. In the worst case, a short circuit or a “thermal event” is possible due to the water leaking into the battery. The latter is the abstract description for a fire. According to Audi, however, the probability of a leak is extremely low. A total of 1650 vehicles are affected by the recall.

In November 2019, the Audi e-tron Sportback, a variant with a flat, tapering roof shape, was presented at the LA Auto Show. At the same time also the variant with the steeper rear received a slight technical revision.
In January 2020, Audi applied for short-time work due to bottlenecks at the suppliers to install the batteries at the Brussels plant, where the e-tron is manufactured. Contracts of at least 145 temporary workers are not renewed, and up to 250 temporary workers may be affected.
Technology
Body
The five-seater sport utility vehicle is 4.90 meters long, 1.94 meters wide (without a mirror) and 1.63 meters high (including a roof antenna). The frontal area of the vehicle is 2.65 m². The curb weight of the vehicle with driver is 2565 kg. The dimensions of the “Sportback” variant differ only in height, which is only 1616 mm here. With regard to the external dimensions of the vehicle is thus between the current series of the models Q5 and Q7.

Electronic exterior mirrors are available for an additional charge. The image of the cameras attached to the side of the vehicle is displayed on two monitors in the two front doors. In this configuration, this decreases drag coefficient value from 0.28 to 0.27. The Sportback achieves a drag coefficient of 0.25. The electronic exterior mirrors are not yet approved for all markets worldwide; the e-tron is optionally available with conventional exterior mirrors or with cameras.
Drive
The drive takes place via the asynchronous motors integrated in the front and rear axles with a system output of 300 kW (408 PS) and a maximum torque of 664 Nm in boost mode, which is limited to a duration of 8 seconds, in the “S” speed step. If the vehicle is not operated in boost mode, the peak power available for over 60 seconds is 265 kW and the maximum torque is 561 Nm.

The maximum power on the front axle is 135 kW (184 hp) and 165 kW (224 hp) on the rear axle (each in Boost mode). The top speed of the vehicle is electronically limited to 200 km/h; it accelerates from 0 to 100 km/h in 5.7 seconds in boost mode, otherwise in 6.6 seconds. The continuous power of the vehicle drive is 100 kW. The spur gear differential for front and rear axle drive comes from Schaeffler.
On the front axle, the input and output shafts are parallel to each other (APA250: asynchronous motors, parallel arrangement, 250 Nm torque), on the rear axle, the output shaft is guided through the drive shaft in a coaxial design (AKA320: asynchronous motors, coaxial arrangement, 320 Nm torque). The gearbox, asynchronous motors and power electronics are assembled at Audi Hungaria in Györ (Hungary).
Brake system
As standard, the vehicle has internally ventilated brake discs that are actuated electro-hydraulically. The diameter of those used on the front axle is 375 mm in combination with six-piston fixed calipers, on the rear axle 350 mm with single-piston floating calipers. They are used if the negative acceleration should be more than 0.3 g (corresponds to 2.9 m / s²). Below that, the vehicle decelerates using electrical recuperation. Since Audi assumes that the friction brakes rarely have to be used in everyday driving and would therefore start to rust, the vehicle has an automatic brake cleaning function. The car is the first pure electric mass-production vehicle with brake-by-wire.
Battery
The lithium-ion battery of the Audi e-tron 55 quattro with a nominal energy content of 95 kWh, of which 83.6 kWh can be used, consists of 432 pouch cells from the Korean supplier LG Chem and weighs a total of 699.4 kg. The battery contains 36 modules, each with 12 cells. A cell has a capacity of 60 Ah. Overall, the parallel connection of four cells results in a nominal capacity of 240 Ah. The nominal voltage of the battery is 396 V. As part of a small revision, the usable energy content was increased to 86.5 kWh at the end of 2019.
The Audi e-tron 50 quattro has a lithium-ion battery with a nominal energy content of 71 kWh, of which 64.7 kWh can be used. This battery consists of 324 prismatic cells from the Korean supplier Samsung SDI.
The battery of the Audi e-tron is actively cooled and heated using a water-glycol circuit.
Charger
The e-tron can be charged via the onboard charger with up to 11 kW (3 × 230 V, 16 A three-phase) at a three-phase connection (AC). A second charger will be available as an option from 2020, resulting in a charging capacity of up to 22 kW (3 × 230 V, 32 A three-phase). The maximum charging power at CCS quick charging stations is 150 kW (DC) for the Audi e-tron 55 quattro and 120 kW (DC) for the Audi e-tron 50 quattro.
Energy consumption
Depending on the equipment, the range of the model equipped with a 95 kWh lithium-ion battery is up to 417 kilometers after the WLTP cycle. The energy consumption according to WLTP is 22.6–26.2 kWh / 100 km. In the fall of 2019, the range was the e-tron quattro 55 km up to 436 increases, the power consumption by WLTP is now 22.4 to 26.4 kWh / 100 km. The equivalent fuel efficiency measured by EPA is 74 MPGe, with an amount of energy of 33.7 kWh corresponding to one gallon of gasoline.
Guarantee Scheme
When buying a new vehicle, Audi grants a manufacturer’s warranty of 2 years without limit on the mileage for all models, which can be extended to up to 5 years and a maximum mileage of 150,000 km with a follow-up warranty in the form of chargeable special equipment.
Production
A total of 43,376 Audi e-trons were produced in 2019.