The Electronic Parking Brake or EPB is a technology in motor vehicles that uses actuators on the rear wheel brake and a control unit to replace the conventional parking brake.

Technology
The electronic parking brake replaces the mechanical parking brake in the automotive industry.
With the conventional parking brake, the driver activates a mechanical device with his foot or hand, which generates a locking force on the rear brake system via cables. The operator generates an individual mechanical force with an actuation unit (hand or foot operated). This is transmitted to the rear brake system via mechanical cables. Here a force is exerted on the brake disc or drum. In the case of very heavy vehicles, a separate drum brake is often used in order to achieve the necessary holding forces.
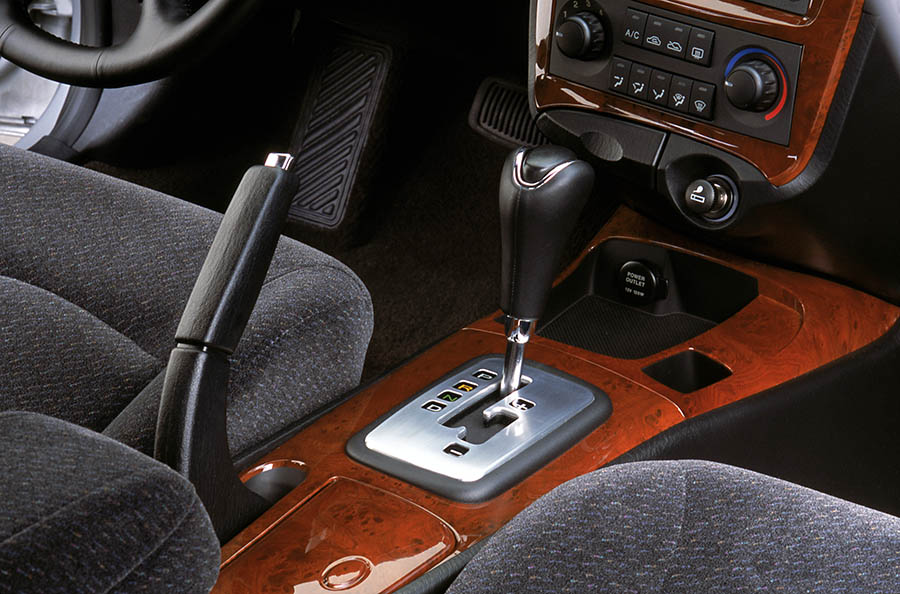

Three systems are currently available for the electronic parking brake. What they all have in common is the replacement of the mechanical operating lever with an electrically switching operating unit.
Cable Puller System
An actuator (motor-gearbox unit, usually with an integrated electronic control) tensions the mechanical cables, which then generate the tensioning force in the rear brake system as with the conventional parking brake. The advantage of this system is that the EPB can be integrated into an existing vehicle structure, since the installation space can be freely selected and this system works with both drum and disc brakes.
Motor on Caliper System
This is a system in which additional small motor-gear units (also called direct actuators) mounted directly on the brake caliper actuate the brake pistons of the rear brake calipers and thus generate the necessary locking force. There are no more cables in this system. The system is very easy to integrate into a vehicle, but only works with disc brakes.
Electric drum brake
This system is used for very heavy vehicles. A motor-gear unit activates a separate drum brake that generates the clamping force. With this system there are no longer any cables.
How it works
The electronic parking brake is another step towards the implementation of a fully electronic braking system. With their help, it is possible to implement additional comfort functions, such as assisted starting on the mountain. This function can also be made possible by other driver assistance systems.
A handbrake lever or handle including Bowden cable, which is usually located in the center console of a vehicle, is completely dispensed with. The EPB is operated via a button and thus opens up new possibilities for vehicle manufacturers in the design of the interior.
Benefits and advanced features
Vehicle interior design:
- Replacement of the hand lever with a freely configurable electrical control unit, the vehicle interior can be designed individually.
- More free space for the center console.

Redundant braking system (dynamic state) with additional fall-back levels:
- Actuation of the electronic parking brake while driving (safe dynamic deceleration over all four wheels).
- Very safe braking even in poor conditions.
Security functions:
- Automatic retensioning (hot brakes lead to a loss of clamping force with a mechanical parking brake, i.e. the braking force decreases in the cooling phase. The electronic parking brake compensates for the loss.)
- The vehicle is always parked with maximum clamping force (always safe – with a mechanical parking brake, the driver determines the holding force – incorrect operation due to insufficient braking force is excluded).
Comfort functions:
- Automatic release when moving off (drive away release – DAR).
- Automatic closing of the parking brake when the ignition key is removed.
Advanced features:
- Auto-hold function (the parking brake is automatically activated when the vehicle is stationary).
- Additional function (prevents the vehicle from rolling away unintentionally).
Maintenance-free:
- The cable EPB compensates for the wear on the brake linings, so maintenance is not required.
Cons
- Decoupling of the driver and the associated loss of control and function.
- Pull-in and release times at 1 second, which is slightly slower than a manual parking brake.
- Total failure of the function if the electrical power supply fails.
- Higher complexity.
- Costs, whereby the costs of the electronic parking brake are approaching those of the conventional handbrake more and more due to the increasing spread in the market.
- “Gentle” release not possible or dependent on programming, which makes starting on slippery surfaces very difficult.
- Systems that work with additional motor-gear units mounted directly on the brake caliper increase the unsprung mass on the affected wheels.
- Brake cannot be used to drift the vehicle.









“Cannot be used to drift the vehicle” should be first in the cons list lol