The spark plugs in VW Atlas Cross Sport are responsible for generating sparks that ignites the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chambers of the engine. Driving your Atlas Cross Sport with bad spark plugs can damage the engine or the catalytic converter, so you must act urgently to avoid more expensive repairs.
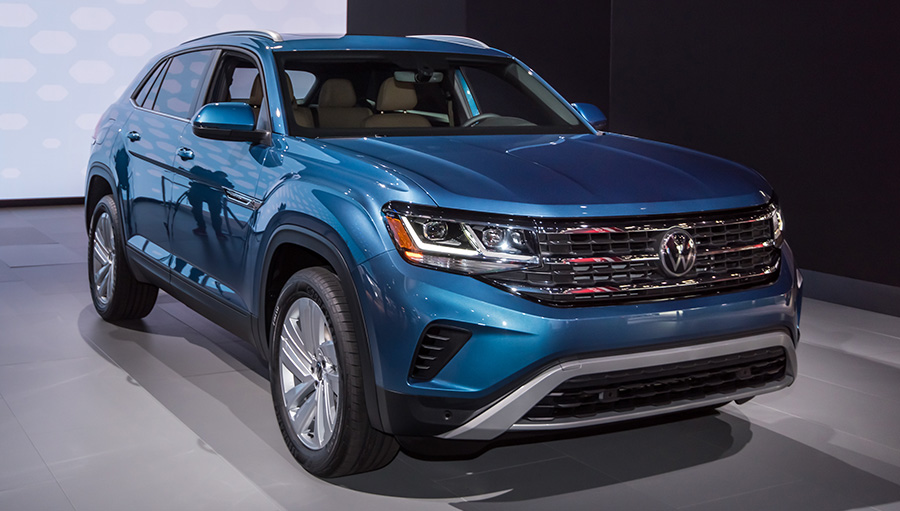

The most common signs of bad spark plugs in VW Atlas Cross Sport are poor acceleration or hesitation, rough idle, engine misfires, poor fuel economy, check engine light illuminates, engine knocking noise, and sometimes hard starting. In worst case scenario, if the spark plugs are in really bad condition, the engine will not start.
Symptoms
Check engine light illuminates due to misfires
When one or more of the spark plugs start to fail or has failed in your Atlas Cross Sport, it will cause the engine to misfire and the check engine light may illuminate in the instrument cluster. To perform further diagnostics, you will need to connect OBD2 scanner to your vehicle. If you see any error code from P0300 to P0312, it indicates that there are misfires in the engine. However, it can happen that there are no error codes. In case of doubt, check the condition of the spark plugs and replace them if found defective.
Poor acceleration
If the spark plugs are not generating sparks properly, the engine will lose power. When you press the gas pedal in your Atlas Cross Sport, the vehicle may hesitate to accelerate and it will take longer to reach your desired speed.
Rough idle
Another indication of bad spark plugs in VW Atlas Cross Sport is rough idle. The engine will not run smooth when idling, you may also feel vibrations in the cabin.
Poor fuel mileage
Excessive fuel consumption is a common sign of bad spark plugs in Atlas Cross Sport. If your vehicle is getting significantly lower gas mileage than usual, its time to inspect the condition of the spark plugs.
Hard starting
When the spark plugs go bad, it is going to take longer for the engine to turn over and start. The ignition system in your Atlas Cross Sport will have to work a lot harder to be able to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chambers.
No start
Your Atlas Cross Sport may not start if the spark plugs have worn too much, or if they have been contaminated due to improper combustion. For example, a malfunctioning MAF sensor or O2 sensor can cause the engine to misfire or run rich that can cause carbon fouling of the spark plugs.
What causes spark plugs to go bad in VW Atlas Cross Sport?
A spark plug is like a canary in a coal mine for the engine. Inspecting the condition of the spark plugs in your Atlas Cross Sport can help you determine the health of the engine.
Normal wear
Replacing spark plugs is part of regular maintenance since its a wearing part. If you do not replace the spark plugs in your Atlas Cross Sport at the prescribed interval, they will wear out and stop producing sparks properly. Read the owners manual or maintenance schedule of your vehicle to know when to change them.

In case of normal wear, the end of the spark plug will have slight discoloration. Also, the center electrode and/or ground electrode tip may have worn away, increasing the gap between them.
Rich air-fuel mixture / carbon fouling
If there is too much fuel in the combustion chambers of the engine, it can foul the spark plugs. When this happens, the end of the spark plug will have dry layer of gray or matte black (sooty looking) carbon deposits evenly distributed over the electrode and the porcelain. Before installing new spark plugs in your Atlas Cross Sport, you must fix the problem that is causing the engine to run rich, otherwise your new spark plugs will get fouled again.

Common causes of engine running rich in VW Atlas Cross Sport are defective or dirty MAF sensor, bad upstream O2 sensor, malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator, leaky injector and faulty engine coolant temperature sensor.
Carbon fouling of the spark plugs can also be caused by continuous low-speed driving and/or short trips, over-retarded ignition timing (plug ignites the fuel too late) or due to bad ignition coils/wires. Using spark plugs with too cold heat range can also cause carbon fouling, in this case the firing end does not reach the self-cleaning temperature of approximately 450°C (842°F).
Engine oil leak
An oil leak in the combustion chambers of the engine can cause the spark plugs to foul up in Atlas Cross Sport. When this happens, the end of the spark plug will have wet oily or greasy looking gunk over the electrodes, and it will also smell of oil. Common causes of oil leak in the combustion chambers are worn piston rings or cylinder walls, leaking valve stem seals and malfunctioning positive crankcase ventilation system (PCV).

An oil leak in the spark plug well can also cause the spark plug to stop working properly due to contamination of ignition coil. This usually happens due to a leak in the spark plug tube seal in the valve cover.
Coolant leak
Coolant leaking into the combustion chambers of the engine can also foul the spark plugs in Atlas Cross Sport, which is commonly caused by a leaking head gasket or leaking intake manifold gasket.

When coolant burns in the combustion chamber, it can leave a gray or white ashy looking layer of silicates over the end of the spark plug. The appearance can differ depending on the type of coolant you’re using in your vehicle. Monitor the level of the coolant in your Atlas Cross Sport if you suspect a coolant leak.
Fuel additives
Using fuel additives like octane boosters or fuel injector cleaners in your VW Atlas Cross Sport can foul the spark plugs. In this case, there will be orange or reddish brown colored deposits distributed over the firing end of the spark plugs.

This condition can cause the engine to misfire. Normally fuel additives are non-conductive; however some are, and they can create an earth leakage path for the spark if excessive deposits build up at the firing end of the spark plug.
Overheating
Repeated overheating of the spark plug tip can cause premature failure. When a spark plug overheats, the surface on the firing end becomes white and cinder-like deposits form spots on its surface. Electrode melting is a more severe condition of overheating when spark plug temperatures reach 800 degrees Celsius (1,472°F) or more. The firing end of the plug may glow red hot from excessive heat and induce abnormal combustion prior to sparking (pre-ignition), which can damage the engine.

Causes of overheating include over advanced ignition timing, excessively lean air-fuel mixture, insufficient coolant or engine oil, excessive turbo pressures (in turbo equipped vehicles), fuel octane rating too low (causing engine knocking), inadequate fuel quality and insufficient plug tightening.
How to replace spark plugs in Atlas Cross Sport
If the spark plugs go bad in your VW Atlas Cross Sport, you must replace them with new ones. You don’t necessarily have to visit a workshop to replace the spark plugs, you can do it at home by following a few simple steps. Before you begin, make sure the engine is cold to prevent burn injury.
- Disconnect the electrical connectors from the ignition coils.
- Remove the ignition coils.
- Remove any dirt or debris inside the spark plug tubes using compressed air.
- Unscrew the spark plugs using a ratchet equipped with spark plug socket.
- Check the electrode gap on new spark plugs using a gap gauge. Make sure the gap is according to the specs mentioned in the owners manual of your VW Atlas Cross Sport.

- Screw in the new spark plugs by hand and tighten it up with a torque wrench.
- Reinstall the ignition coils and their electrical connectors.
Recommended video
Which type of spark plugs to use in Atlas Cross Sport?
There are four main types of spark plugs: copper, platinum, double platinum and iridium. Generally all the spark plugs have similar type of internal components, but where they differ is at the tip where the spark happens. Check the owners manual of your VW Atlas Cross Sport to see which type of spark plug is recommended for your engine, as it can differ depending on the engine type and model year of the vehicle.
You can generally upgrade to higher quality spark plugs. For example, if your owners manual recommend platinum, you can upgrade to iridium spark plugs. But never downgrade to lower quality plugs.
Copper: This is the most basic and least expensive spark plug. The tip is made of copper, which is highly conductive, therefore creating a strong spark. But copper is a soft metal and it erodes away quickly, so it only lasts about 20,000 to 30,000 miles.
Platinum: They are a little more expensive than the copper plugs. In this case, as the name suggests, the tip is made of platinum, which is not as conductive as copper but is harder and more resistant to wear. Platinum plugs can last from 60,000 to 100,000 miles.
Double Platinum: In this type of spark plug, the center electrode tip is made of platinum and there is also another piece of platinum on the ground electrode. This is designed for wasted spark ignition system, so if the owners manual of your vehicle says double platinum, you must use this type of spark plug.

Iridium: This is the most expensive type of spark plug. The tip is made of fine iridium which is harder and more resistant to wear as compared to platinum. Iridium has a melting point of up to 4,471°F (2,466°C), which is almost three times the melting point of copper. Iridium plugs can last 100,000 to 120,000 miles.
Use OBD2 scanner for diagnosis
Since VW Atlas Cross Sport is equipped with on-board diagnostics (OBD), a fault diagnosis can provide initial indications of where the malfunction is located.
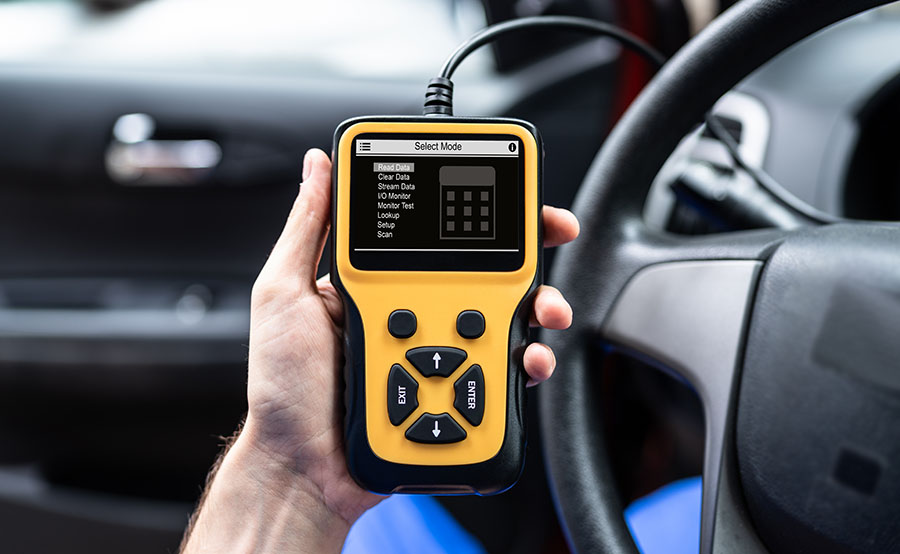

To begin troubleshooting, you must first connect the diagnostic tool to your Atlas Cross Sport. The OBDII connector is usually located under the dashboard. With the tool connected, turn on the ignition. Most diagnostic devices then ask for some information about the vehicle. It is important that you enter this 100% correctly, otherwise the result of the search may be inaccurate. In addition to the vehicle make, model, and engine type, you usually also have to type in the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). Since some OBD codes are manufacturer-specific, the scanner will be able to give you more accurate information if you enter more details about your Atlas Cross Sport.
Conclusion
If you see noticeable loss of performance or engine hesitation with high fuel consumption in your VW Atlas Cross Sport, you should definitely check the condition of the spark plugs and ignition coils. Nevertheless, it is recommended to strictly follow the maintenance schedule of your vehicle and replace the spark plugs at prescribed intervals for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Do not wait for the spark plugs to go bad before replacing them as it can damage the engine or the catalytic converter.
In any case, it is advisable for laypersons to visit a workshop. A professional mechanic can swiftly diagnose the problem for you.