The O2 sensor in Toyota 86 monitors the level of oxygen in the engine’s exhaust gases and reports the data to the control unit that continuously adjusts the air to fuel ratio in the engine to achieve maximum efficiency. Driving your 86 with a bad oxygen sensor can damage the engine or the catalytic converter, so you must act urgently to avoid more expensive repairs.
The most common signs of bad O2 sensor in Toyota 86 are slow acceleration, loss of power, irregular idling, engine hesitation or jerking when accelerating, high fuel consumption, higher tailpipe emissions, foul odor from exhaust, check engine light illuminates, and sometimes stalling.
Upstream and downstream O2 sensors
Upstream O2 sensors are important for engine performance
There are multiple O2 sensors in Toyota 86, how many depends on vehicle configuration and model year. But the most important one is the upstream O2 sensor, the one that is closest to the engine, usually in the exhaust manifold. The upstream O2 sensor helps in maintaining proper air to fuel ratio in the combustion chambers for maximum fuel efficiency and engine performance. Any fault in this sensor can cause all sorts of performance issues in your 86.

Downstream O2 sensors do not affect engine performance
The downstream O2 sensor in 86 is located further down the exhaust system, after the catalytic converter, and is responsible for measuring the level of pollutants passing through the catalytic converter. The main purpose of downstream O2 sensor is to ensure that the catalytic converter is functioning properly. If this sensor goes bad, it does not have any affect on the engine performance, but the check engine light may illuminate and you may see error codes related to catalyst efficiency.
Bad O2 sensors lead to catalytic converter failure
Faulty oxygen sensors are the leading cause of premature catalytic converter failures. If you suspect a problem with O2 sensor in your 86, you should act immediately and get it checked by a professional mechanic. Because O2 sensors are relatively cheap compared to the price of catalytic converters, which can easily cost you over a thousand dollars to replace.

How to check for bad O2 sensor in 86?
If there is any fault in the oxygen sensor, it usually illuminates the engine check light in the instrument cluster of Toyota 86. You can diagnose the problem by connecting an OBD2 scanner to your vehicle. If you see any error code from P0130 to P0135 or from P0150 to P0155, it indicates a problem with the upstream oxygen sensor. You can also perform a continuity test on the connector of the sensor with a multimeter to check if the heater circuit is broken.
How to replace O2 sensor in 86?
You don’t necessarily have to visit a workshop to replace oxygen sensor in your Toyota 86. All you need is a wrench for this replacement job. Make sure the engine is cold before replacing the sensor to prevent burn injury.
- Locate the O2 sensor to be changed.
- Unplug the connector of the sensor.
- Unscrew the O2 sensor with a wrench.
- Apply anti-seize lubricant to the threads of the new sensor.
- Screw in the new O2 sensor by hand and tighten it up with a wrench.
- Connect the electrical plug of the new sensor.
Recommended video
What causes O2 sensors to fail in Toyota 86?
All O2 sensors fail over time since it is a wearing part. There is no fixed time limit for when they fail, but they typically last over 100,000 miles in 86. However, they can fail much sooner due to contamination. For example, due to silicates entering the exhaust system after coolant burns in the engine due to a leaky head gasket, or phosphorus from excessive oil consumption due to worn piston rings or valve seals.
What happens if you keep driving with a bad O2 sensor?
Driving your Toyota 86 with a bad O2 sensor can cause sluggish and rough acceleration, along with high fuel consumption and emissions. And if you continue driving for several months, it may lead to engine damage or catalytic converter failure which can cost thousands of dollars to fix or replace.
Can a bad O2 sensor cause poor acceleration?
If the oxygen sensor goes bad in 86, it does not send correct measured values to the engine control unit. The optimal amount of fuel can no longer be calculated which results in either too little or too much fuel injected into the combustion chambers. The engine runs too “lean” or too “rich”. Since a rich or lean condition robs a vehicle of power, a bad oxygen sensor can cause poor acceleration.
Can a bad O2 sensor cause shaking?
A faulty O2 sensor can certainly cause shaking or vibrations in Toyota 86 when driving. When the O2 sensor goes bad, it causes improper air-to-fuel mixture in the combustion chambers which can cause the engine to shake, these vibrations can be felt in the cabin of the vehicle when driving.
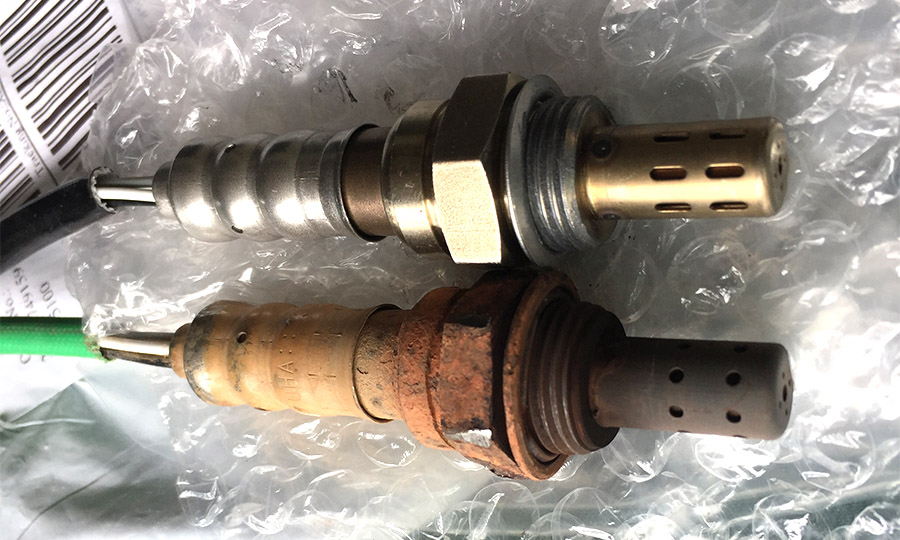

Will a new O2 sensor improve gas mileage?
According to EPA, replacing a bad oxygen sensor can improve fuel economy by as much as 40 percent. So if your 86 develops a greater thirst for gas, you should definitely consider checking or replacing O2 sensor, especially if the vehicle has racked up more than 100,000 miles.
Use OBD2 scanner for diagnosis
Since Toyota 86 is equipped with on-board diagnostics (OBD), a fault diagnosis can provide initial indications of where the malfunction is located.
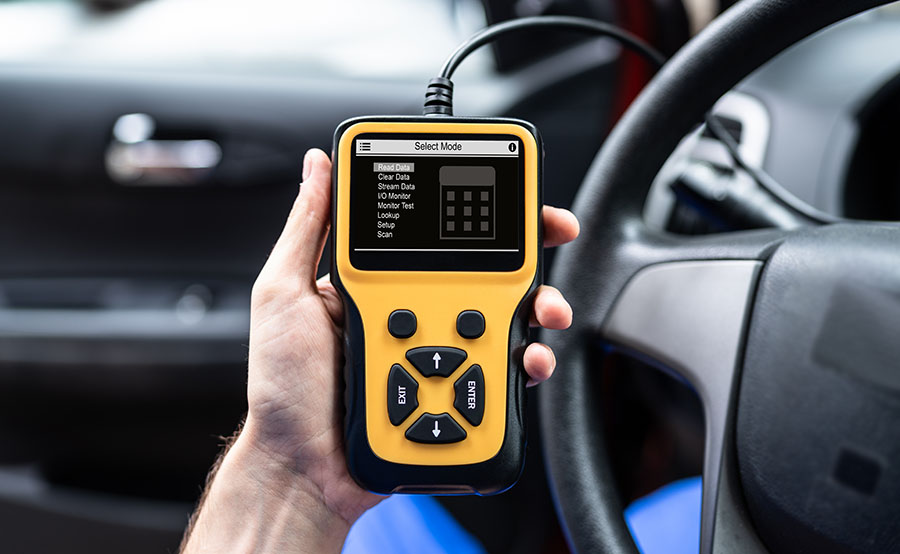

To begin troubleshooting, you must first connect the diagnostic tool to your 86. The OBDII connector is usually located under the dashboard. With the tool connected, turn on the ignition. Most diagnostic devices then ask for some information about the vehicle. It is important that you enter this 100% correctly, otherwise the result of the search may be inaccurate. In addition to the vehicle make, model, and engine type, you usually also have to type in the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). Since some OBD codes are manufacturer-specific, the scanner will be able to give you more accurate information if you enter more details about your 86.
Diagnostic error codes for O2 sensors
Following are all the error codes that indicate a problem with an oxygen sensor.
- P0130 = 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
- P0131 = 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
- P0132 = 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
- P0133 = 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
- P0134 = 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
- P0135 = 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
- P0136 = 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
- P0137 = 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
- P0138 = 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
- P0139 = 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
- P0140 = 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
- P0141 = 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
- P0142 = 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
- P0143 = 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
- P0144 = 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
- P0145 = 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
- P0146 = 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
- P0147 = 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
- P0150 = 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
- P0151 = 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
- P0152 = 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
- P0153 = 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
- P0154 = 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
- P0155 = 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
- P0156 = 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
- P0157 = 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
- P0158 = 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
- P0159 = 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
- P0160 = 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
- P0161 = 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
- P0162 = 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
- P0163 = 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
- P0164 = 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
- P0165 = 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
- P0166 = 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
- P0167 = 02 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
Conclusion
If you see noticeable loss of performance or engine hesitation in your Toyota 86 with high fuel consumption, a defective upstream oxygen sensor should definitely be considered. Even if your vehicle is not showing any signs of trouble, it is recommended to replace the upstream O2 sensor after 100,000 miles for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
In any case, it is advisable for laypersons to visit a workshop. A professional mechanic can swiftly diagnose the problem for you.